Getting started with Traefik

At my new workplace we are making heavy use of docker and docker-compose. In order to make all of the containers talk to each other we use Traefik (opens new window). So in order to actually use it I need to understand how Traefik works. Let's dive into it together! 🤓
# What is Traefik? 🤔
The documentation puts it that way: Traefik is an open-source Edge Router that makes publishing your services a fun and easy experience. It receives requests on behalf of your system and finds out which components are responsible for handling them.
See the official documentation (opens new window) for more information.
# Why do I need Traefik? 🤔
I have multiple docker-compose environments on my machine. Before Traefik I could only have one environment running at a time. This is because each environment was using port 80 and 443 for the HTTP and HTTPS traffic. Now that I have Traefik I can have multiple environments running and Traefik will route traffic to the correct environment.
# Getting started with Traefik! 🥳
Let's start our journey by creating a simple Traefik setup that will route port 80 to one of two nginx containers. Don't worry, we will go over it step by step 👍
Before you can start tho you will need to install docker and docker-compose.
Once that is done, create the following docker-compose.yml file in a dedicated directory, eg. tutorial/reverse-proxy.
version: '3'
services:
reverse-proxy:
# The official v2 Traefik docker image
image: traefik:v2.6
# Enables the web UI and tells Traefik to listen to docker
command: --api.insecure=true --providers.docker
ports:
# The HTTP port
- "80:80"
# The Web UI (enabled by --api.insecure=true)
- "8080:8080"
volumes:
# So that Traefik can listen to the Docker events
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
Now navigate into the newly created directory and execute the following to start the container through docker-compose.
docker-compose up -d
If this is the first time that you are running Traefik, docker will need to pull the image and boot it up. So don't worry if it takes a while 😅
Once the container are running, you should be able to access the following url.
https://localhost:8080/ (opens new window)
If you have other containers running that block this port you might not be able to reach the service. To bring down all your docker containers run
docker container stop $(docker container ls -aq).
If this does not work because there are still other networks blocking, try running
docker network prune.
If this still does not work you probably have another service of some kind running on port
80or8080🙈
If everything worked out, you should see the following in the browser.
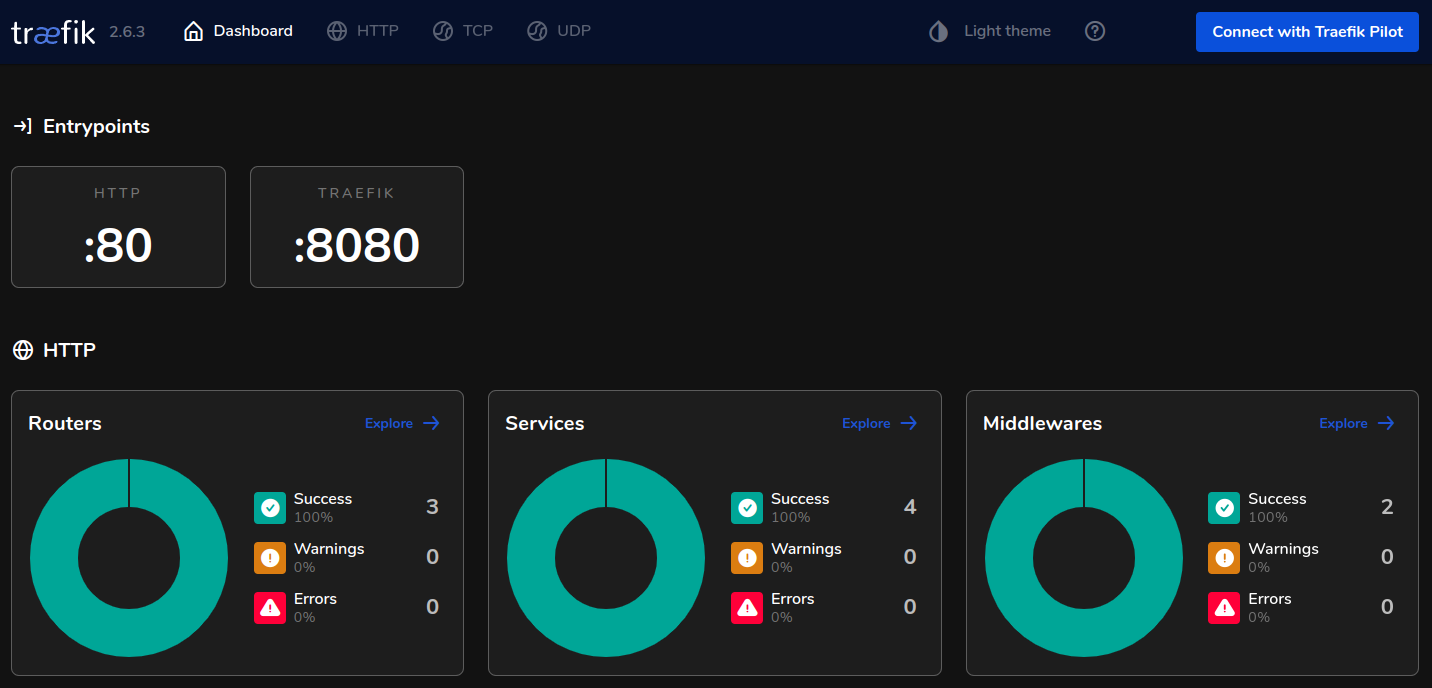
Awesome! Traefik is running and you can access the dashboard through port 8080 🥳
But what about port 80? 🤔
Doesn't look so good 😥 But that's ok 😉 We are not serving anything on that port yet 😅
Before we can do so, we need to create a network that both environments can sit in. Let's update the tutorial/traefik/docker-compose.yml file so it looks like this:
version: '3'
networks:
# configuring the default network of Traefik
default:
internal: false
name: reverse-proxy
services:
reverse-proxy:
# The official v2 Traefik docker image
image: traefik:v2.6
# Enables the web UI and tells Traefik to listen to docker. Also,
# we don't want to expose containers per default.
command:
- "--api.insecure=true"
- "--providers.docker"
- "--providers.docker.exposedByDefault=false"
ports:
# The HTTP port
- "80:80"
# The Web UI (enabled by --api.insecure=true)
- "8080:8080"
volumes:
# So that Traefik can listen to the Docker events
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
Now let us create a Nginx (opens new window) container.
Create a new directory on the same level as tutorial/reverse-proxy, eg. tutorial/nginx-localhost and create the following docker-compose.yml file within that directory.
version: '3.8'
networks:
reverse-proxy:
external: true
services:
nginx-localhost:
image: nginx:latest
networks:
- reverse-proxy
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.docker.network=reverse-proxy"
- "traefik.http.routers.nginx-localhost.rule=Host(`localhost`)"
Navigate into the tutorial/nginx-localhost directory and execute the following to start the container through docker-compose.
docker-compose up -d
Now go visit http://localhost (opens new window) and you should see the nginx default page.
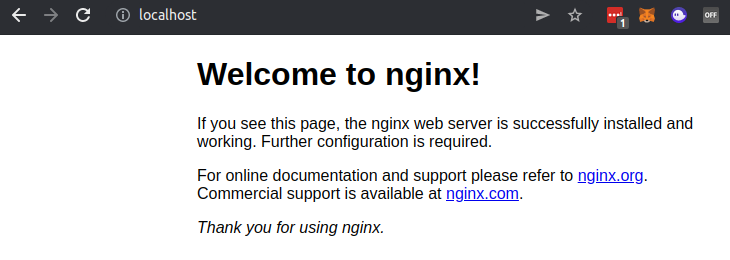
Awesome! Now we have our first docker environment that we are exposing on port 80 🥳
Let's create another one! 🚀
Our next nginx container is going to be provided through the hostname second.local. Since we do not have a DNS server in our environment we are going to create an entry in our /etc/hosts file. Add the following to your /etc/hosts file:
127.0.0.1 second.local
Now create another folder for the second nginx setup, eg. tutorial/second-nginx and create the following docker-compose.yml file within that directory.
version: '3.8'
networks:
reverse-proxy:
external: true
services:
second-local:
image: nginx:latest
networks:
- reverse-proxy
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.docker.network=reverse-proxy"
- "traefik.http.routers.second-local.rule=Host(`second.local`)"
As you can see, it is almost the same file as for the first nginx container. The only difference is that we are now using the hostname second.local instead of localhost and the service has a different name so we can separate them in the traefik labels - see the last label to see what I mean 🧐
Now navigate into the tutorial/second-nginx directory and execute the following to start the container through docker-compose.
docker-compose up -d
You should now be able to access the second nginx container through http://second.local (opens new window).
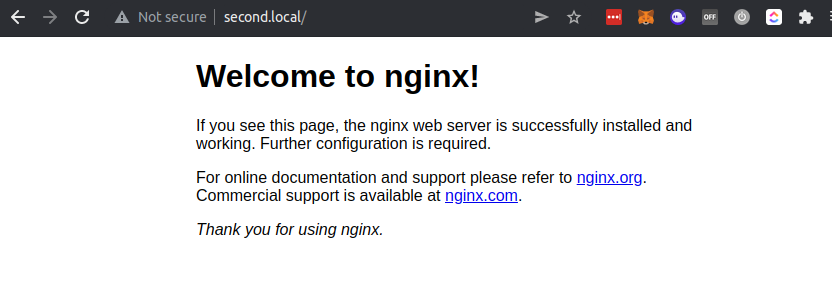
Ta-da! We have two containers running on port 80 🎉
If you want to connect new containers you only need to add the following labels to the given service in your docker-compose.yml file.
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.docker.network=reverse-proxy"
- "traefik.http.routers.SERVICE-NAME.rule=Host(`SERVICE-HOST`)"
And that's basically it! 🎉
If you want to check out more tutorials on how to use Traefik, check out the Traefik documentation (opens new window) or the GitHub repository (opens new window) that I'm using to experiment with Traefik and other cool stuff. You can also find all the files of this article in this repository.
See you next time! 🤓

